The global digital health market is expected to reach $1.3 trillion by 2025, driven by the increasing adoption of technology in the healthcare industry. There are currently over 300,000 digital health companies worldwide, and this number is expected to continue to grow in the coming years says CBInsights.
As the demand for digital services in design continues to rise, the supply in this field is also expanding. We'll delve into the fundamental principles of digital lead design. These principles are designed not only to enhance your ability to generate high-quality leads through marketing efforts but also to optimize the impact of product design on lead conversion.
What is Design Principles in Digital Healthcare?
Your patient or customer has certain psychological principles that can be reinforced with the right product principles and implemented through design.
Design principles are like the building blocks that go beyond just making things user-friendly. They also include important ideas about how the actual products should work. These principles cover things like making sure digital healthcare products can grow as needed, work well with other systems, stay secure, and show information in a way that's easy to understand. Whether it's making things easy for users or keeping information safe, these principles are the key to making healthcare technology better for everyone.
The Process of Identifying Design Principles in Healthcare
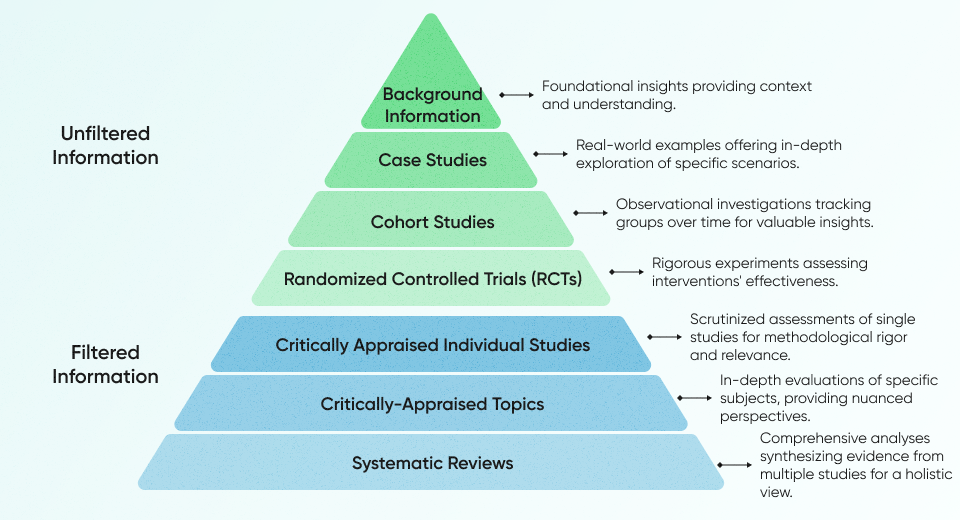
Levels of evidence in research serve as a hierarchical framework, categorizing studies based on their design and methodological rigor. This system aids in evaluating the strength and reliability of research findings. In the context of digital healthcare design principles, these levels play a pivotal role in informing decision-making and shaping user-centric solutions. More often, this is done by product managers, and ready-made research is given to designers to create an effective user experience (UX).
Aligning design decisions with robust evidence, such as systematic reviews and meta-analyses, enables designers to build a foundation rooted in thorough and validated research. Higher-tier evidence, like randomized controlled trials (RCTs), guides designers in creating user-centric solutions with proven effectiveness. Cohort studies contribute to a nuanced understanding of user behavior over time, empowering designers to make informed decisions based on observed trends.
When it comes to mitigating risks, case-control studies aid designers in identifying potential issues tied to specific design choices, allowing for the integration of mitigation strategies into the design process. Moreover, evidence from case series and reports, while recognizing its preliminary nature, inspires designers to explore inventive concepts and contribute to the evolution of design practices.
Even at the lowest evidence level, expert opinions play a valuable role in iterative design processes, offering insights in areas where empirical evidence may be limited or emerging. This incorporation of evidence levels ensures that digital healthcare design principles are not only based on evidence-backed practices but also adaptable to the evolving landscape of user needs and experiences.
Key Design Principles in Digital Healthcare
The way healthcare works is changing quickly because of digital transformation. This brings new chances to make patient care better, easier to access, and more affordable. But for these digital changes to work well and last, we need to follow some important design rules. These rules make sure we focus on what patients need, what healthcare providers need, and what the whole healthcare system needs.
Let’s take a look at the main design principles in digital healthcare.
User Research
As mentioned above, the product or project manager collects information about the market, and the main cases and passes it on to the designer. Based on this, the designer can already form a user-centered user experience using data and design thinking.
Beginning the design process involves creating user personas and categorizing them into segments. Following this, the focus shifts to identifying user needs and pain points, with special attention given to navigation, interface, colors, and essential features for the product. It's only after completing the design research that the creative process can move into brainstorming and the creation of initial sketches.
The fundamental principle a designer should consistently bear in mind is to prioritize users, in this instance, patients, and apply strategic design thinking.
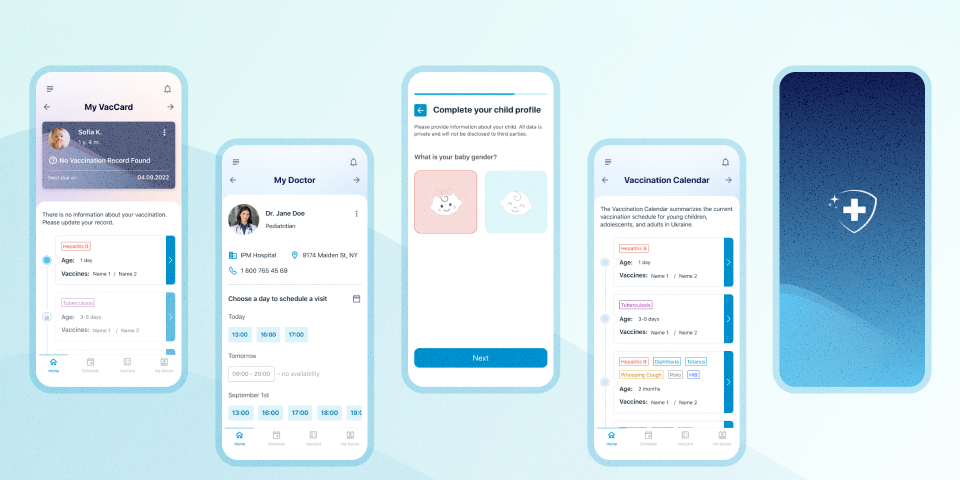
Consider VaccApp, our client, as an example. VaccApp is a solution tackling the challenges parents face in keeping track of their child's vaccinations. It simplifies vaccination details, digitizes records for convenience, raises awareness about recommended shots, and helps parents stick to vaccination schedules through a user-friendly platform.
During the design research, we found that general vaccination information can be unclear for those without a medical background. Most vaccination records are kept in paper documents, and many parents aren't well-informed about recommended shots. Additionally, parents, responsible for their child's vaccinations, may forget and fall behind schedule.
To address these issues, our design includes features like a Personal Vaccination Card, Vaccine Details, an individual vaccination plan, pediatrician recommendations, and information on upcoming and recommended vaccinations, along with the ability to update and book appointments with the doctor.
Thanks to our research-driven design solutions, VaccApp makes it easier for parents to stay on top of their child's vaccination schedule, minimizing the risk of missed vaccinations and ensuring timely protection against diseases.
Collaboration Between Clinicians and Patients
Design features prioritize efficient data input and retrieval for clinicians, coupled with a patient-oriented interface delivering easily understandable health information, treatment plans, and avenues for seamless communication with healthcare providers.
This can include features like secure messaging, virtual consultations, and patient portals that provide access to medical records, test results, and educational resources.
To enhance collaboration between clinicians and patients in digital healthcare design, start by understanding the unique needs of both user groups through in-depth research. Craft tailored user personas for clinicians and patients, identifying their preferences and pain points. Prioritize features that streamline data exchange, providing clinicians with efficient data input and retrieval tools. For patients, focus on a user-friendly interface delivering clear health information, treatment plans, and seamless communication channels with healthcare providers. Incorporate strategic design thinking to address concerns such as data privacy and security, ensuring a trustworthy and collaborative digital environment. Regularly gather feedback from users to iterate and refine the design for ongoing improvement.
For example, at Movadex we can do A/B testing and conduct pilot testing and evaluation of the collaborative features to assess their effectiveness in improving communication, shared decision-making, and patient outcomes.
Legal and Safety Issues
Designers should know that healthcare employers are facing more responsibility for their employees' exposure to COVID-19 and pandemic-related issues. Lawsuits are increasing, claiming safety rule violations. It's crucial for a safe workplace, following CDC and OSHA guidelines for infection control and worker training. Many lawsuits involve problems like retaliation and denying leave. Designers need to understand federal acts like the Families First Coronavirus Response Act (FFCRA) and the Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act (WARN) for job-protected leave and notice requirements. Being aware of these rules is important for designers to handle these challenges well.
Data security regulations vary depending on the geographic location of your product's users. For instance, if your product is intended for users in the United States, it must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Similarly, products targeting Canadian users should align with the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), while those catering to European Union residents must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
To bolster data security and ensure your product meets the necessary standards, designers can consider incorporating features like end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication. These measures play a vital role in protecting user information and demonstrating your commitment to safeguarding sensitive data.
Integrated Care
The coordination of care across various healthcare settings is a key aspect. Design principles can prioritize features that streamline care coordination, such as appointment scheduling, medication management, and remote monitoring.
Patients benefit from a personalized journey, accessing features like tailored care plans, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders through a user-friendly interface. This integrated approach enhances care coordination, fostering collaboration among providers and improving the overall healthcare experience for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Future Trends in Digital Healthcare Design
Advancements in Remote Healthcare Solutions
The landscape of healthcare is evolving with the rise of remote solutions, such as video communications and telemedicine consultations. These innovations redefine accessibility by enabling patients, regardless of location, to connect with healthcare professionals for high-quality consultations.
DTx, or digital therapeutics, is special medical software that helps people handle specific diseases and stop them from getting worse. It's always checked by doctors and can be used on smartphones or tablets.
The digital therapeutics market size was USD 5.53 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from USD 6.77 billion in 2023 to USD 28.66 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 22.9%.
Mental Health Apps
Mental illnesses are common in the United States. It is estimated that more than one in five U.S. adults live with a mental illness (57.8 million in 2021).
So the global mental health apps market size was accounted at USD 5.19 billion in 2022 and it is expected to reach around USD 26.36 billion by 2032. America plays a crucial role, often being in the top tier for such applications. This means that a significant number of downloads and purchases originate from America.
Take, for instance, the popular meditation app Calm, which generated an estimated revenue of $355 million in 2022. This clearly indicates a growing trend, making it worthwhile to explore this market and conduct thorough design research.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics is a key design trend in digital healthcare, featuring tools like AI-operated symptom checkers and enhanced medical alarms/alerts. These tools support healthcare professionals by swiftly assessing initial symptoms, addressing critical patient needs, and sending timely alerts for urgent conditions, such as seizures or hypo-/hyperglycemia, in patients at home.
For instance, predictive modeling helps hospitals anticipate whether a patient might return within a certain number of days after being discharged.
For example, at the University of Kansas Health System, they used this predictive tool for patients with diabetes. They found that problems like not getting follow-up care and where the patient goes after leaving were causing people to come back to the hospital. So, they made plans to fix these issues. As a result, the number of people coming back to the hospital went down from 25% to 13.9% in less than a year.
Forecasting appointment
Healthcare predictive analytics can assist hospitals in estimating the likelihood of a patient missing their appointment by considering factors like past no-shows or the distance from the clinic. This enables doctors to enhance patient scheduling. Clinics can adopt reminder systems or provide transportation options for patients at higher risk of missing appointments.
For example, Boston Children’s Hospital researchers successfully predicted patient no-shows with an 83% accuracy using a machine learning algorithm, as highlighted in Nature. Boasting a false alert rate below 17%, this approach emerges as a valuable tool for healthcare providers, addressing financial and health-related concerns by reducing no-show appointments. The retrospective study, conducted in an academic pediatric teaching hospital with a 20% no-show rate, effectively navigated challenges such as missing patient data and local weather considerations. The model's adaptability in handling incomplete patient information positions it as a promising solution for optimizing scheduling systems, reducing patient wait times, and facilitating targeted reminders, ultimately enhancing healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rapid evolution of digital health, forecasted to reach a staggering $1.3 trillion by 2025, signifies a dynamic landscape with immense potential. Fundamental principles in digital healthcare design serve as the linchpin for effective product development, ensuring user-centricity, adaptability, and the seamless integration of evidence-based practices.
The process of identifying these design principles involves a hierarchical approach, employing levels of evidence in research. The tiered framework, including systematic reviews, meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, and other studies, informs decision-making and shapes user-centric solutions. Also, key design principles encompass various facets, from user research to collaboration between clinicians and patients, legal considerations, and the integration of care across healthcare settings. These principles not only prioritize user needs but also navigate complex legal and safety issues, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA, PIPEDA, and GDPR.
Future trends in digital healthcare design, like remote solutions, digital therapeutics, mental health apps, and predictive analytics, are transforming the way we approach healthcare. For instance, Movadex's work with healthcare companies demonstrates how collaboration can bring about innovative solutions for better healthcare.




