Have you ever contemplated the adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) in your company? СВS News says that BYOD usage statistics show 67% of employees use their own devices for work.While this approach can offer cost-saving and flexibility benefits, it also brings forth critical challenges, such as data security and employee productivity. This article explores the pivotal decision that business owners face when considering BYOD, shedding light on the potential advantages and pitfalls they should carefully evaluate.
What does BYOD mean?
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) refers to a policy or practice in which employees are allowed to use their personal smartphones, tablets, laptops, or other devices for work-related tasks and to access company networks, systems, and data.
How Does a BYOD Policy Work
BYOD enables greater flexibility and convenience for employees but also raises concerns about data security, management, and privacy, which organizations must address through specific policies and security measures when implementing BYOD policy.
Here's a short bring your own decice policy plan for businesses.

Remember to define which functions, such as email, databases, and applications, employees can access from their devices. Also, detail any costs that the organization may reimburse employees for, such as data plans or other work-related expenses.
It's crucial to work closely with IT, legal, and HR experts to create a comprehensive and customized policy that aligns with your company's specific requirements and risk tolerance.
Types of BYOD Policies
BYOD policies can enhance your ability to attract new talent. As many individuals favor the use of their personal mobile devices, companies that offer this flexibility may gain a competitive edge during the recruitment process when compared to organizations that mandate the use of uniform company-provided smartphones and laptops for all employees.
There are several types of BYOD policies, each tailored to meet different organizational needs and security requirements. Here are some common types:
- Standard BYOD Policy: This is the most basic form of BYOD policy. It outlines the basic rules and guidelines for using personal devices for work purposes, covering aspects like eligible devices, security measures, and acceptable use.
- Restricted BYOD Policy: In this type of policy, certain restrictions and limitations are imposed on the use of personal devices. This may include limiting the functions and applications employees can use or imposing stricter security measures.
- Unrestricted BYOD Policy: This policy is characterized by a high degree of freedom for employees. It allows for broader usage of personal devices for work, with fewer restrictions on applications and functions.
- Stipend BYOD Policy: Under this policy, organizations provide employees with a stipend or reimbursement to cover some of the costs associated with using their personal devices for work. It helps offset expenses like data plans or device maintenance.
- COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally-Enabled) Policy: This policy is a variation of BYOD where the company provides the device, but employees are allowed to use it for personal purposes as well. It combines elements of both corporate-owned and BYOD policies.
- Containerization Policy: In this approach, a separate, secure container is created on the employee's personal device to isolate work-related data and applications. This ensures a clear separation between personal and work data.
- Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) Policy: While not strictly BYOD, CYOD allows employees to select from a set of pre-approved company-owned devices, giving them some choice while maintaining control over device standards.
- Industry-Specific Policies: Certain industries, like healthcare or finance, have unique security and compliance requirements. BYOD policies in these sectors must align with industry-specific regulations and best practices.
- Temporary or Project-Specific Policies: Some organizations create temporary BYOD policies for specific projects or periods when the use of personal devices is particularly advantageous. These policies are in effect for a limited duration.
- Remote Work BYOD Policy: With the rise of remote work, many organizations have specific BYOD policies for remote employees. These policies address unique security and connectivity needs for remote workers.
The most common type of BYOD policy is the Standard BYOD Policy. This policy typically outlines the basic rules and guidelines for using personal devices for work-related purposes within an organization. It often covers aspects such as eligible devices, security measures, acceptable use, and the responsibilities of both employees and the company.
Standart BYOD Policy Example
By adhering to this policy, you can aim to strike a balance between harnessing the productivity and convenience that personal devices offer while safeguarding the security and confidentiality of company data. This policy represents our commitment to creating a dynamic and secure digital workspace for all members of the [Company Name] team.
1. Introduction
This Standard BYOD Policy outlines the guidelines and rules for the use of personal mobile devices for work-related activities at [Company Name]. The purpose of this policy is to promote productivity, flexibility, and convenience while upholding the security and confidentiality of company data.
2. Eligible Devices
- Eligible devices for use in the BYOD program include smartphones (iOS, Android), tablets (iOS, Android), and laptops (Windows, macOS).
- Devices must be no more than three years old and equipped with the latest operating system and security updates.
3. Password Protection
- All devices must be protected with a password, PIN, pattern, or biometric authentication.
- Passwords should be strong, unique, and changed every 90 days.
4. Authorized Use
- Employees are allowed to access company email, calendars, and approved applications from their personal devices.
- Personal use is permitted but should not disrupt work responsibilities.
5. App Restrictions
- Unauthorized applications that could compromise security are not allowed.
6. Two-Factor Authentication
- Employees must implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for all company accounts and applications that require it.
7. Data Control
- [Company Name] reserves the right to remotely wipe company data from a lost or stolen device.
- Upon employee departure, all company data will be removed from their personal device.
8. Policy Agreement
- All employees are required to read, understand, and sign this BYOD policy before participating in the program.
- Employees will be promptly informed of any updates or changes to the policy.
9. Cost Reimbursement
- [Company Name] will reimburse employees for work-related expenses, such as data plans, as per the company's expense policy.
10. Ongoing Training
- Regular training and updates on security best practices and BYOD policy changes will be provided to employees.
11. Enforcement
- Non-compliance with this policy may result in disciplinary action, including the revocation of BYOD privileges.
12. Review
- This policy will be reviewed and updated annually to ensure it remains aligned with best practices and technology advancements.
Why is BYOD Important
Forbes says that 61% of Gen Y and 50% of 30+ workers believe the tech tools they use in their personal lives are more effective and productive than those used in their work life.
Therefore, if you are in doubt whether you should introduce BYOD in your company, here are some points that will help you with the choice.
- Boosted Productivity: BYOD lets employees use their own devices for work, which often means they can work where and how they're most comfortable. For instance, they can draft an email response on their smartphone during a commute, which wouldn't be possible with a company-provided device.
- Cost Savings: With BYOD, employees use their personal gadgets, saving the company money on purchasing and maintaining devices. The organization may reimburse them for work-related expenses, like a portion of their phone or internet bill.
- Global Workforce Integration: For example, a team member in New York and another in London can collaborate effectively using their own devices.
- Security and Environmental Benefits: BYOD policies typically come with robust security measures to protect company data. This ensures that sensitive information remains safe. Moreover, fewer company-owned devices mean less electronic waste, contributing to a greener environment.
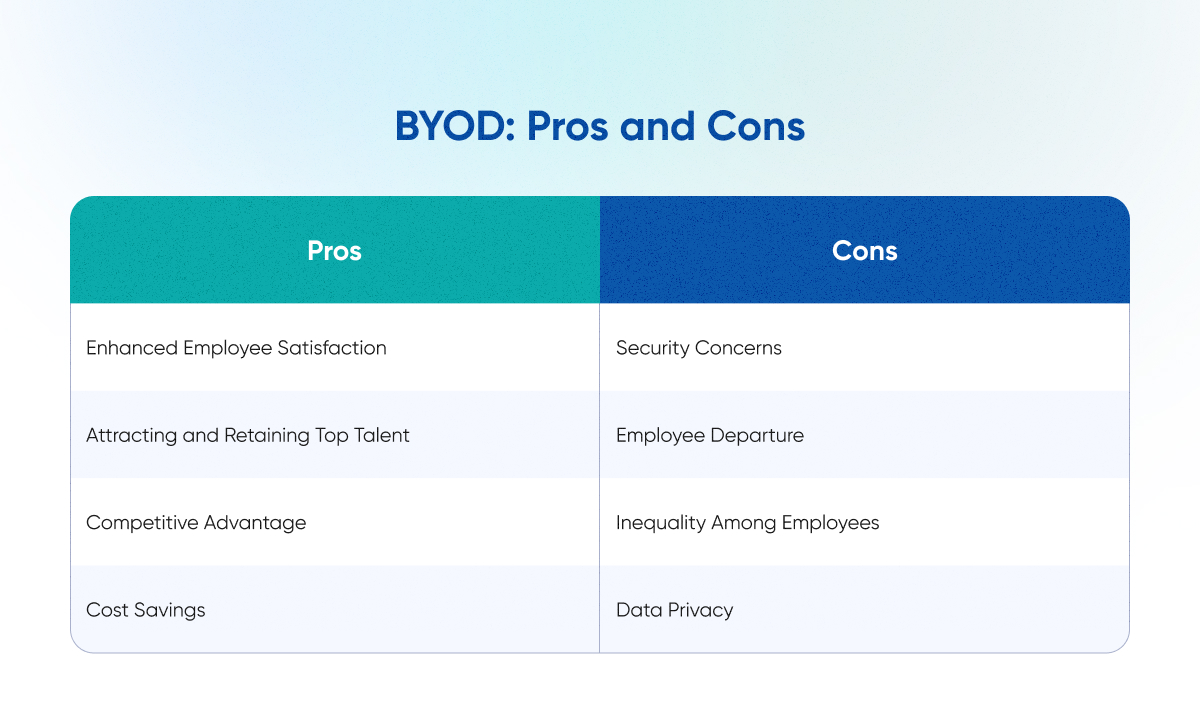
BYOD Pros and Cons
It would seem, according to preliminary data, that the BUOD has only one plus. But let's look at it from another perspective as well.
Pros
1.Enhanced Employee Satisfaction
When employees have the freedom to use their preferred devices, it often leads to increased job satisfaction. For example, Citrix reported a 92% employee satisfaction rate after implementing BYOD, showcasing how such policies can contribute to a happier workforce.
2.Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
Companies that offer BYOD as an option can attract and retain tech-savvy employees. For example, IBM found that 57% of tech-savvy professionals consider the availability of BYOD programs as a factor when choosing an employer.
3.Competitive Advantage
Companies that embrace BYOD early can gain a competitive advantage. They can adapt more swiftly to changing technology trends and meet the evolving needs of the workforce. For example, Coca-Cola Enterprises improved its field sales operations by equipping its salespeople with BYOD devices, gaining a competitive edge in the industry.
4.Cost Savings
BYOD can lead to significant cost savings for companies. For instance, Cisco reported saving approximately $2 million a year on cell phone expenses after implementing a BYOD policy. Employees typically bear the cost of purchasing and maintaining their devices, and companies may only need to reimburse them for work-related expenses.
Cons
1.Security Concerns
BYOD can introduce security risks. For instance, a study by Check Point Software found that 42% of companies experienced a security breach due to unsecured BYOD devices. Furthermore, approximately 30% of companies identify security apprehensions as the primary factor deterring them from embracing BYOD practices.
2.Employee Departure
When employees leave the company, it can be challenging to ensure the complete removal of company data from their personal devices. Failure to do so poses a security risk. A study by Osterman Research found that 89% of organizations had employees leave with company data on their personal devices which leads bring your own device security issues.
3.Inequality Among Employees
Not all employees can afford the latest and most secure personal devices, potentially creating inequality and resentment among the workforce.
4.Data Privacy
Employee-owned devices may not meet the same data privacy standards as company-owned devices. This can lead to privacy breaches and legal issues. An example is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which imposes strict data protection regulations that can be challenging to enforce on personal devices.
Best BYOD Programs in 2023
Choosing a bring-your-own device is a flexible matter, and it is impossible to choose one single program for everyone. Therefore, before choosing your software, let's break down the main terms that will help you decide what exactly you need.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
It ensures device security by enforcing security policies, safeguards data by enabling remote wipes, manages and secures applications, controls network access based on device security, tracks compliance and costs, aids in troubleshooting, offers user authentication, maintains a device inventory, and enforces BYOD policies.
For instance, a multinational corporation with remote and on-site employees allows them to use their personal smartphones and tablets for work purposes. To maintain security and manage these diverse devices effectively, the company implements a mobile device management.
The Best Mobile Device Management (MDM) Programs
-
Esper is an MDM solution designed primarily for Android devices.
-
Scalefusion MDM secures and manages a wide range of devices, including laptops, smartphones, tablets, digital signage, point-of-sale systems (POS), and rugged devices.
-
Miradore is an MDM tool that ensures cost-effective security and compliance across all mobile devices, making it possible to secure, track, enroll, and manage iOS, macOS, Windows, and Android devices from a single location.
-
Addigy is a specialized Apple device management tool, Addigy empowers IT administrators to monitor Apple devices in real-time, covering macOS, iOS, iPad, and TV devices.
-
Jamf Pro is a comprehensive mobile device management system specifically designed for Apple macOS desktops and iOS devices, offering a complete solution for Apple device management.
Mobile Application Management (MAM)
Mobile Application Management (MAM) is a solution that focuses on securing and managing the applications on personal devices used for work. MAM is particularly useful in scenarios where companies want to ensure that employees can access and use specific business apps securely on their personal devices without compromising data security.
For example, a healthcare institution may implement MAM to ensure that doctors and nurses can securely access patient records and medical apps on their personal tablets and smartphones while adhering to strict regulatory requirements for data protection and patient confidentiality.
The Best Mobile Application Management (MAM) Programs
-
MaaS360 Mobile Application Management is a robust MAM program known for its comprehensive features and compatibility with a variety of devices.
-
Worx Home is a Citrix product offering secure mobile application management, particularly for workplaces seeking efficient app control and protection.
-
Hexnode UEM is a versatile program that excels in mobile application management while also providing unified endpoint management for various devices.
-
Digital.ai provides MAM capabilities, contributing to secure and streamlined application management for a variety of mobile devices and platforms.
Containerization
Containerization is a technology that creates secure, isolated environments on personal devices, segregating work-related data and applications from personal content.
For example, a financial institution may use containerization to ensure that financial transactions and sensitive customer information are isolated from an employee's personal apps and content.
The Best Containerization Programs
-
Docker, a market leader in containerization, provides a powerful platform for creating, deploying, and managing containerized applications.
-
Google Kubernetes Engine, known for its scalability and reliability, offers a managed Kubernetes service, making container orchestration and management easier.
-
CoreOS specializes in containerization and provides solutions for securing, updating, and managing containerized applications.
-
LXC, an open-source containerization solution, offers a lightweight and efficient way to create and manage system containers, promoting resource isolation and security.
Secure File Sharing and Collaboration Tools
Secure File Sharing and Collaboration Tools are software solutions that enable users to share and collaborate on documents, files, and data in a secure and controlled manner. They are essential in scenarios where organizations need to facilitate teamwork and data exchange while ensuring data security and compliance. For example, a multinational corporation may utilize a secure file sharing and collaboration tool like Microsoft OneDrive for Business to enable its employees, scattered across different regions, to collaborate on projects, share important documents, and maintain version control securely.
The Best Secure File Sharing and Collaboration Programs
-
Dropbox is a widely-used secure file sharing and collaboration program that offers cloud-based storage, sharing, and collaboration features with strong security measures.
-
Google Drive, part of Google Workspace, provides secure and collaborative cloud storage, document editing, and real-time collaboration tools for businesses and individuals.
-
Notion is a versatile program that combines secure file sharing with project management, knowledge management, and collaborative workspace features.
-
Microsoft OneDrive, integrated into Microsoft 365, offers secure cloud storage and collaborative document editing, making it a popular choice for businesses looking to combine productivity and data security.
The Tips to a Successful BYOD Policy
1.Establish Company-Wide Policy
It should outline the rules and expectations regarding device usage, security, and data management.
2.Be Clear About Which Devices You Want to Support
Clearly define which types of devices and operating systems your organization is willing to support: iOS or Android, Windows or Macintosh?
3.Provide Support and Assistance for Your Employees
Create an internal portal where employees can find FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and contact details for the IT helpdesk. This ensures that employees have access to assistance when they encounter technical issues on their personal devices.
4.Respect Employee Privacy
Personal content will remain entirely private, and no personal data will be accessed or modified by the company.
5.Determine your BYOD cost sharing model
Decide how you'll handle costs associated with BYOD, such as device purchase, data plans, and maintenance. Whether it's full company reimbursement, partial reimbursement, or no reimbursement, a clear cost-sharing model should be established and communicated to employees.




